Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory systemic disease. In more than 80% of the patients the lung is one of the primarily affected organs. Pulmonary sarcoidosis has previously been considered to be mainly a T helper type 1- and macrophage-driven disease. Recently, a novel population of T follicular helper-like (also known as T peripheral helper) cells which promotes B cell responses in inflamed non-lymphoid tissues has been described. These cells lack the classical Tfh markers Bcl-6 and CXCR5, but express high levels of the two key B cell helper molecules CD40L and IL-21.
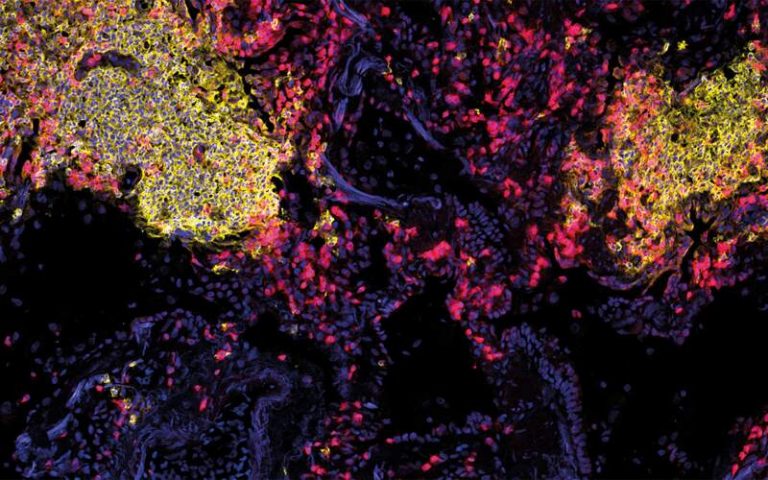
This new study demonstrates for the first time the presence of Tfh-like cells in the lungs of pulmonary sarcoidosis patients. They co-produce high levels of IFN-γ and IL-21 and provide potent B cell help in vitro. In the lung tissue, they are found in large lymphocytic infiltrates in close contact with B cells, indicating that they drive the local generation of plasmablasts. Consistent with this, BAL fluid from sarcoidosis patients contains high levels of immunoglobulins.
These findings highlight an underappreciated role of T cell / B cell collaboration in sarcoidosis. More over, elevated frequencies of circulating Tfh-like cells in peripheral blood may be a useful marker for monitoring sarcoidosis disease activity.
- Laura Bauer, Lisa Jasmin Müller, Sarah M. Volkers, Frederik Heinrich, Mir-Farzin Mashreghi, Clemens Ruppert, Leif E. Sander, and Andreas Hutloff. Follicular Helper–like T Cells in the Lung Highlight a Novel Role of B Cells in Sarcoidosis.
- Shaikh M. Atif and Andrew P. Fontenot. T–Follicular Helper–like Cells in Sarcoidosis: Lending a Helping Hand.
- Andreas Hutloff. T Follicular Helper-Like Cells in Inflamed Non-Lymphoid Tissues.